edit I am an idiot, who uploaded the image link as the URL. The original source should now be accessible
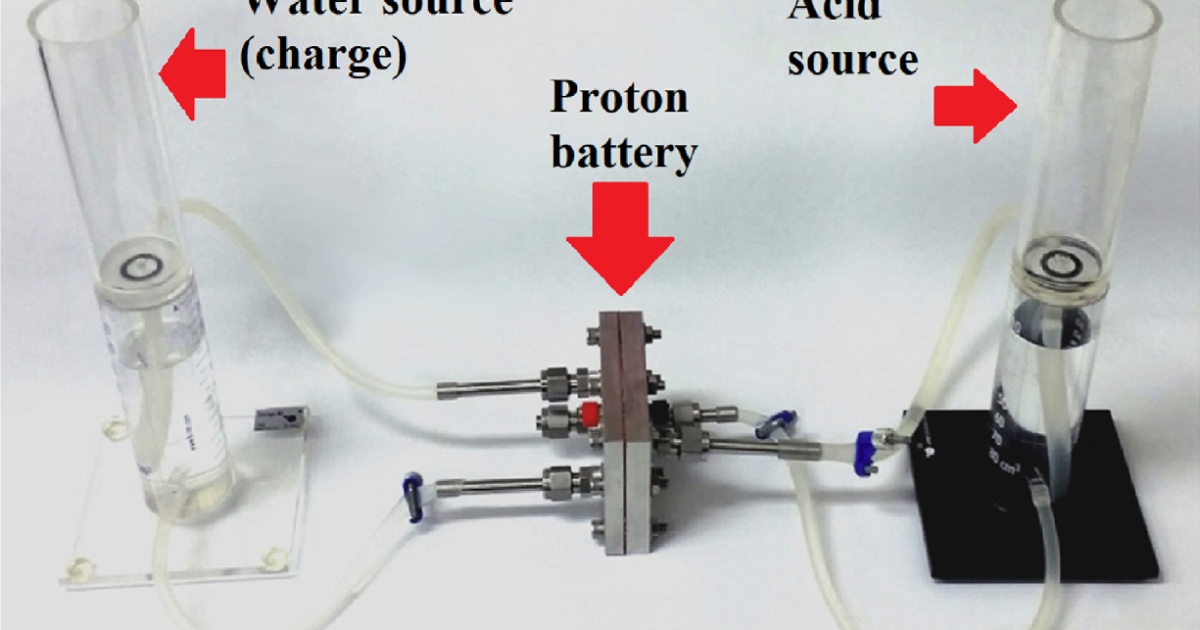
RMIT engineers say they’ve tripled the energy density of cheap, rechargeable, recyclable proton flow batteries, which can now challenge commercially available lithium-ion batteries for capacity with a specific energy density of 245 Wh/kg.
Please sir, may I have the sauce?
I’ve edited the post, thankfully someone beat me to replying so you weren’t left hanging. My apologies!
“you don’t need lithium or any other exotic metals”
This is really good news.
Lithium isn’t exactly exotic, it’s the third most common element in the universe.
25th most common on Earth and most of it is in the ocean, which we don’t have a good extraction method for yet.
Edit: how did you come up with Lithium being the 3rd most common in the universe? Oxygen is 3rd and Lithium is 44th most abundant universally.
Huh, I guess I was wrong. Lithium was one of the first elements created in the universe, and it turns out it’s lack of abundance in the current universe is a problem.
Wow that’s really interesting.
to be fair I thought the same! that’s weird 🤯
Battery tech exists in a variety of stages. We have been using Li-ion for ages but there are two technologies coming out this year and next which are very much real (from CATL the worlds leader in battery sales) one of which you can buy today.
You can buy Sodium Ion batteries already, search for it on aliexpress and you’ll see the cells are for sale and BYD is already selling cars with it in. Its similar power in weight and density as Li-ion but it doesn’t catch on fire and its a lot more environmentally friendly. Its good a chance of being the main battery used for home/grid storage and cars and other big battery uses, it also lasts a lot of cycles something like 6000-8000 so it will work for decades and its cheap at $50/KWH (li-ion is more like $130).
The other type is a Li-ion advancement into solid state that is due next year and it doubles the power density. That is probably going to end up in laptops and phones and some high end cars with massive range or smaller/lighter batteries where the increased cost for power density is worth it. Not yet at commercial volumes it is well past the theoretical stage however and very much something that can be manufactured already.
All this battery tech in the lab might very well be in the mix in the future but we don’t need them to pan out with Sodium Ion filling that space and quite cheaply due to the abundance of salt. I think for grid storage reflux batteries might see a resurgence for their versatility but it remains to be seen if they become price competitive. Li-ion as we use today is very soon to be replaced thankfully.
Found a good video article on Na-Ion battery technology; https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RQE56ksVBB4
So according to that article Na-Ion energy density is comparable to the LFP type of Li-Ion battery. That’s about 20% lower than the more common types you see in consumer products and EVs. LFP has much longer cycle life and lower fire hazard so it’s used where weight and space are less of a concern. However it still has the same cost and materials issues.
Na-Ion is well poised to replace LFP. The advantage is lower cost and more environmentally friendly materials. Unfortunately Na-Ion is not inline to replace the higher energy density types. As it becomes more widely adopted it may improve to the point where it can so there’s hope for it.
Here is an alternative Piped link(s): https://piped.video/watch?v=RQE56ksVBB4
Piped is a privacy-respecting open-source alternative frontend to YouTube.
I’m open-source, check me out at GitHub.
You can buy Sodium Ion batteries already,
You see a lot of stories about the next great battery tech. I’ve been seeing them for years, but still Li-Ion is the ubiquitous tech.
Even if energy density is only comparable, a battery with lower fire hazard and increased longevity is sorely needed. Li-Ion batteries simply wear out too fast. Considering the replacement cost (especially for EV applications), its a huge advantage for consumers. Then there’s a bonus of it being cheaper and more environmentally neutral which is also a big deal.
Of all the proclamations of a better battery, Na-Ion sounds like it might actually be a reality. That would make me happy to be rid of Li-Ion batteries once and for all. The only advantage they have is high energy density, they’re a fail on every other front.
it also lasts a lot of cycles something like 6000-8000 so it will work for decades
Not good enough for the next 10 years.
Energy density and charging speed must, and will, improve by much more.
The good news is that funding is finally being given for it so advancement will happen
Most applications assume max 2 charge/discharge cycles per day, don’t they?
And where space is not an issue, a cheaper option could be favourable? Im afraid I don’t understand both your points
Im afraid I don’t understand both your points
Of course you can’t LOL, if cycles per day and cheap is all that you can think, because I simply haven’t talked about these two topics.
Does this exist as a consumer product yet?
From what the article said, most definitely not. But, it doesn’t look very complex in terms of scaling / manufcaturing it and they say they want to get it to market quickly.
This is a research paper, so it’s gonna be at least a couple of years until ot could be seen in products. However the battery uses hydrogen, it’s effectively an alternative to fuel cells, so the use case would be in vehicles rather than yout phone. That being said, hydrogen fuel infrastructure is almost non-existent right now.
the battery uses hydrogen, it’s effectively an alternative to fuel cells,
No, and No.
You want to read the article linked above.
You want to read the article linked above.
We don’t do that here
Is the infrastructure relevant though? As I understand it, the battery is charged by splitting water (H2O) into Oxygen and Hydrogen atoms (instead of H2 molecules, hence the name proton battery) and instead of compressing and cooling it, having a solid structure in which to store the protons. When drawing energy from the battery the opposite process takes place. So basically it is both an electrolyser when charging and a classic fuel cell when discharging with the storage of hydrogen (protons) being integrated in the same battery through a porous solid (mainly carbon). To quote from the article: >It looks like more of a battery competitor than a fuel cell competitor, though.
Next to the advantages they cite (energy and power density, abundant and environmentally unproblematic materials, recyclability, not explosive) I do wonder about the density in terms of volume. If they are bigger in size, they could constitute a better solution for big energy storages within the grid or at home, where now many are using lithium ion batteries.
You should definitely read the linked article. You’re right about it being for your car, not your phone, but seriously, read the article.
Others downvote you and say “read the article”, but not giving arguments.
I read the article and it is not clear what is the advantage… looks like less pressure is needed than other types of hidrogen cells, but there are no details.
I agree with you, don’t hold your breath for this. All details would be in first sentence if there was any chance of this becoming reality.
The advantages are, every part of the device can be easily recycled, and the parts to make the charge-holding portion of the battery are less damaging to acquire than in li-ion
The battery uses dark matter, it’s effectively an alternative to nuclear fusion, so the use case would be in space stations rather than yout phazer set to stun.